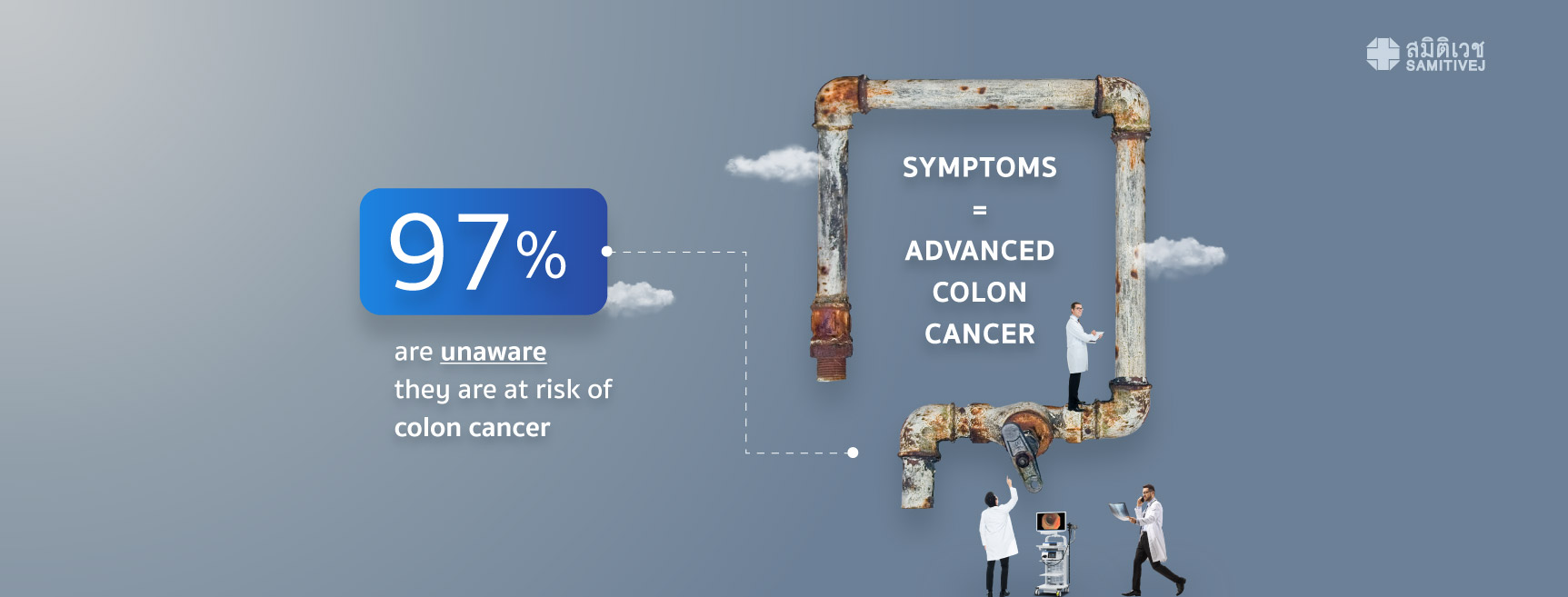
Polyps identified during colonoscopy fall into two categories: hyperplastic polyps, which do not have the potential to develop into colon cancer, and adenomatous polyps, which do have the potential to develop into colon cancer. Samitivej Hospital’s commitment to improving the quality of its colon cancer screening techniques means that we gather the data from each colonoscopy in order to compare the results with the industry standard, as recommended by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE). This standard outlines that of those aged 45 and above, approximately 25% will be found to have adenomatous polyps. This is known as the adenoma detection rate. Detection numbers higher than this average indicate a greater amount of detail offered by the colonoscopy technique being used. Such levels of detail provide a greater chance of identifying polyps that are difficult to detect, such as serrated adenomatous polyps, resulting in an increased level of confidence in the procedure and a higher chance of prevention through the removal of adenomatous polyps before they can become colon cancer. While generally acceptable rates are considered anything greater than 25%, the 55% average adenoma detection rate achieved by GI doctors at Samitivej Sukhumvit is more than twice as accurate as the industry standard as defined by the The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), as of February, 2018)
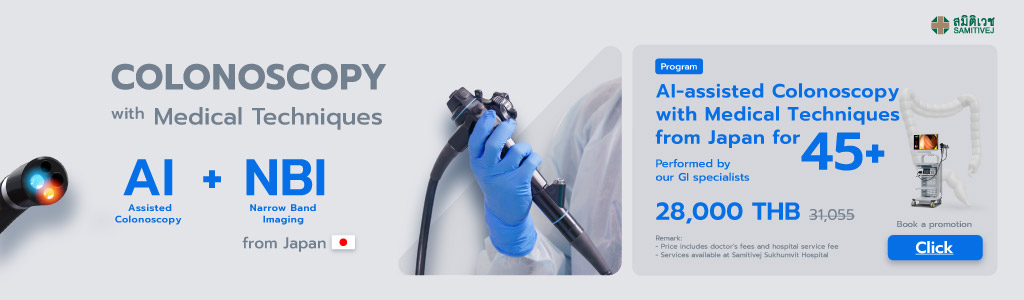
The high adenoma detection rates achieved at Samitivej reflect the high quality of our screening process. The NBI colonoscopy technique we employ, thanks to our longstanding partnership with SANO Hospital, has led to an overall improvement in the quality of our colonoscopy screening for colon cancer. The technique, which utilizes green/blue light rays to identify the presence of polyps, provides doctors with a clearer view of both protruding and serrated adenomatous polyps. This is not possible through the use of regular white light rays. Furthermore, the NBI international colorectal endoscopic (NICE) classification simplifies diagnosis and allows for immediate decisions to be made regarding subsequent treatment. For example, in cases where hyperplastic polyps are found they can be removed, or where adenomatous polyps are identified a sample can be promptly taken in order to confirm whether the polyp is cancerous and which stage the cancer has reached, so that an appropriate treatment plan can be formulated.
Additionally, in cases where an adenomatous polyp measuring more than two centimeters in size is identified, an ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection) can be carried out to remove the polyp instead of a traditional surgical procedure. The result of an ESD is that the patient is able to quickly recover. However, to perform this highly technical procedure a GI specialist must be thoroughly trained and have years of experience. Fortunately, Samitivej has a team of gastrointestinal specialists who have worked alongside medical teams from SANO Hospital to collaborate and share knowledge on numerous case studies.